Determination of national income
Definition and analysis of national income equilibrium
Equilibrium National income, Ye is the national income in the same level of aggregate demand for payment. The level of national income that does not change as long as the composition of aggregate demand for payment remains the same. This is because manufacturers do not want to increase production. Because if the production increase was not sold out the inventory stock is outstanding (D inv> 0) reduced yields products in inventory is reduced (D inv <0) if production has not changed. National income is unchanged.
Analysis YE in the model economy, all have split two ways.
1. National income is equal. Aggregate demand for payment
Y = AD
Called Income - Expenditure approach
M + S + T = I + G +
2. Withdrawal = Injection
M + S + T = I + G + X.
Withdrawal = Injection.
Withdrawal = Injection.
Called the Withdrawal and Injection approach
If the show is 45 ° to the line graph line represents a gross want to spend. (Variable on the vertical axis) is equal to national income (variable on horizontal axis).
Determination National income equilibrium. In case of a closed economy with no government. Involved under the following assumptions.
(1) Economic system, only two regions to the household sector. Businesses do not have savings. By sending income (profits for shareholders) to all households.(2) Free trade with foreign countries.
(3) No government. Therefore, no tax
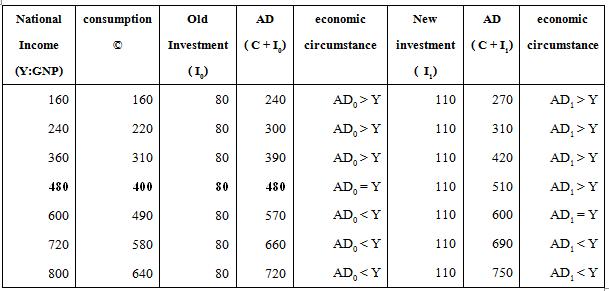
Table 1 the YE in a closed economy with no G Y = AD.
Analysis leakage = injection
Explaining the process to adopt an equilibrium point by considering a leakage is= injection of living conditions2 ways:
(1) Ir = Ip + Iu
(2) Sr = Sp
Table 2 to determine the equilibrium: analysis
of the line was leakage = injection
The changes in levels of income equilibrium
Table 3 changes the equilibrium level of income.
Theories of multiplier and catalyst
Multiplier Is a number multiplied the change of aggregate demand to pay for the changes in national income
Operation of the multiplier. Determination of the multiplier The theory of Keynes about multiplier Conclude that “I (Increase) หรือ G (Increase) > Revenue (T) that result is Y (Increase) not only equal the number (I) and (G) increased only. But an increase of that amount is multiplied by multiplier one. The multiplier is called “the Multiplier”.
Because the expenditure of one person becomes the income of another. So when the President to spend 1 million to hire Mr. B. grow house Mr. B to receive 1 million will be part of the money cost (C) the rest is savings (S) them. Mr. B funds is use it will be paid out as income Mr. C's. as to the fried (Chain effect), and because anyone with money to saving the young one. Therefore, the money paid out in the form of C will decrease and so on until a value close to zero. The following sample table.
The formula for the multiplier in a closed economy without G is divided into two cases.
1. The independent investment.
Observations
1. Is doubly related to the change of variables, including independent expenditures. Independent investment. Government spending and exports.
2. Multiplier effect of positive and negative that is
3. The value of the multiplier. Depending on the value of the MPC
2. a convincing case for investment.
The Accelerator refers to the number shown at the spend on consumption changes will affect the amount of investment or investment incentives will change.
Process of catalysts.
The conditions of work as follows.
1. The value of the acceleration equal to 2, explained that if the cost of consumption increased to 1 unit Make investments or manufacturers investing an additional 2 units or additional investment. It will increase to 2 times. Possibly due to the expanded production. Buy raw materials increased. Investment or set up a new factory up again and so on
2. Net investment refers to investment by different types of equipment no Increase the amount of inventory.
3. The depreciation of the machine at a constant rate. The lifetime of the machine will depreciation to equal every year in the period of 10 years.
4. Set prices for consumer products and capital fixed. Change The value. Spending for consumption and investment costs. Will be a change in the amount of capital is a major product categories.
Table 5 shows the process of catalyst